Let’s start this article on the Law of Demand…
Meaning of Demand-
Demand refers to a desire for anything by consumers with their purchasing power or ability to pay at a particular price and time. Thus, demand in economics implies both the desire to purchase and the ability to pay for a good.
Law of Demand-
The Law of Demand expresses the functional relationship between price and quantity demanded. Thus, according to the Law of Demand, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a commodity or a factor affecting if Ceteris Paribus.
Demand Schedule and Demand Curve-
Noted Economist Alfred Marshall provided the geographical illustration of the law of demand. The law of demand can be illustrated through a schedule and a demand curve. A demand schedule is presented in the table. It will be seen from the demand schedule that as the price of a commodity decreases its quantity demanded increases. The demand curve is a graphical statement or presentation of quantities of a good demanded by the consumer at various possible prices in a period of time.
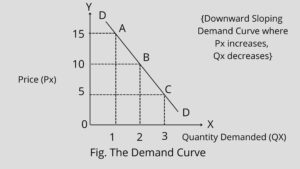
Factors Affecting Demand-
The following are the factors which affects demand for a commodity-
-
Price of the Commodity (Px)-
As the price of a commodity decreases, the quantity demanded of it increases, other things remaining the same.
-
Changes in the Prices of the Related Goods(Pr)-
The demand for a good is also affected by the prices of other goods, especially those which are related to it as a substitute or compliments.
a. Substitute Goods- When the rise in price of a good causes increase in demand for another goods is called substitute goods. For example; tea and coffee.
b. Complementary Goods- The change in the price of any one of them would affect the demand of the other is called complementary goods. For example; If the price of petrol rises, demand for cars falls.
-
Incomes of the people (Y)-
The greater income means the greater purchasing power. As the income of consumers increases the demand for a commodity also increases and vice versa. The effect of income on the demand for a commodity leads to two types of goods. They are-
a. Normal Goods- When with the increase in his income the consumer buys more of a good, it is called a normal good.
b. Interior Goods- When with the increase in income the consumer buys a smaller quantity of a good, it is called an inferior good.
-
Taste and Preferences (T)-
If the items are according to the consumer’s taste, he will prefer them over other commodities.
-
Miscellaneous (U)-
There are some other factors like quality and size of the commodity, composition of the population, discrimination in income distribution, etc. which also determine the demand for a commodity.
Demand Function-
Individual demand for a commodity can be expressed mathematically in the following general functional form-
Qd = f ( Px, Pr, Y, T, U)
where
Px= price of the commodity
Pr= price of the related goods
Y= income of the consumer
T= taste and preferences
U= miscellaneous
Exceptions to the Law of Demand-
Law of demand is generally valid in most of the situations. However, some exceptions to the law of demand have been pointed out.
a. Veblen Effects ( Goods having prestige value)-
Noted Economist Thorstein Veblen propounded the doctrine of conspicuous consumption. According to Veblen, some consumers measure the utility of a commodity entirely by its price. That is for them, the greater the price of a commodity, the greater its utility. For example; diamonds are considered the prestige good for the upper strata of society. The highest the price of a diamond, the higher the prestige value of them and, therefore, the greater utility or desirability of them.
b. Giffen Goods-
Initially proposed by Sir Robert Giffen, with the rise in the price of a Giffen good, its quantity demanded increases. With the fall in its price, its quantity demanded decreases.
Thank you guys, for reading this article on the Law of Demand. I hope you enjoyed it. Please share it with your friends and let me know your feedback in the comment section.
Well arranged article.
THANKS