Let’s read this article on Meaning of Inflation, Types, and Measures…
INFLATION-
Points to be covered-
- Meaning of Inflation
- Types of Inflation-
(A) Based on rate
(B) Based on cause
- Measures of Inflation-
(1) WPI (Wholesale Price Index)-
(2) CPI (Consumer Price Index)-
(3) GDP DEFLATOR-
Meaning of Inflation-
Inflation is the persistent rise in the general price levels of a basket of commodities over the time period. The rate of change is positive in inflation.
Definitions of inflation by some economists-
Coulbor defines inflation as “ too much money chasing too few goods.”
Hawtrey defines inflation as the “issue of too much currency.”
According to Friedman, “Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.”
Crowther has defined inflation as a “ state in which the value of money is falling i.e. the prices are rising.”
According to these definitions, the rise in the price level is caused by an increase in the supply of money. Thus the increase in the supply of money is the cause and the rise in the price level is the effect.
Types of Inflation-
(A) Based on the rate of inflation-
The classification is made on the basis of the ‘speed’ with which the prices increase in the economy.
(1) Creeping inflation- When the price level rises approximately by 0-3% annually, it is known as creeping inflation.
It is the mildest type of inflation which serves as a tonic of development for a backward economy. There are some economists who support creeping inflation in the form of a slow and gradual rise in prices to keep the economy away from stagnation. But there are also some economists who look upon creeping inflation as potentially dangerous. Their view is that if proper control is not exercised over then it is alarming over the time period.
(2) Walking or Tottering inflation- When prices rise moderately and the annual inflation is a single digit between 0-4% per annum it is called walking inflation.
(3) Running inflation- When the prices rise rapidly like a horse at a double rate of speed 10-20% per annum, it is called running inflation.
(4)Galloping inflation or Hyperinflation– when prices rise very fast at double and triple-digit rates from more than 20% per annum, it is known as hyperinflation.
In fact, it is the most dangerous type of inflation. Under this type of inflation, the prices rise every minute. Keynes referred to this type of inflation as true inflation. Example – The most recent example of hyperinflation is in Venezuela.
Hyperinflation creates a situation when a person goes with money in baskets and returns with goods in their pocket.
In fact, these stages of inflation are similar to the stages of the physical development of a child. Thus on the basis of the above analysis, we can say moderate inflation is good for the economy.
(B) Based on cause of inflation-
(1) Demand-Pull inflation-
It is a situation when aggregate demand pulling up the prices as a result of which basket of commodities is costing more.
Reason for arising demand-pull inflation-
- Increasing government expenditure;
- Increasing money supply;
- Parallel money or black money;
- Increasing forex reserves etc.

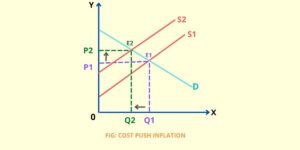
(2) Cost-Push inflation–
A situation where because of various factors of production the cost of the product is increasing which leads to an increase in the prices of the commodities.
Reason for arising cost-push inflation-
- Increase in wages;
- Increase in indirect taxes as GST;
- Increase in the prices of raw materials;
- Supply shocks – because of certain external ad internal events the scarcity of supply is created as the result of price increases, etc.
(3) Structural inflation-
It is caused by deficiencies in the infrastructure and supporting services. It is the feature of developed and developing countries. For example; In the case of India it is caused because of volatility in the prices of agriculture commodities in the market, because of very less warehousing capacity, structural and infrastructural bottlenecks created variation in supply and demand.
Causes-
- food storage constraints;
- scarcity of resources;
- scarcity of foreign exchange reserves etc.
(4) Cartelization-
‘Cartel’ refers to a ‘group of producers’. In cartelization, the price of a commodity is fixed by a group of producers on a consensus basis and they have the authority to hikes the prices according to them. This creates a severe inflation problem. Example- OPEC group. In India it is illegal.
(5) Hoarding– A person in the supply chain is hoarding more than what is allowed. This leads to a decrease in supply whereas demand remains the same. So it creates a shortage of goods in the market due to which inflation arises.
Measures of Inflation-
(1) WPI (WHOLESALE PRICE INDEX)-
- WPI is the inflation rate in the wholesale market (it is a market in which trading is done in huge volumes).
- In the case of WPI, we do not consider services.
- Department of Economic Affairs ( Ministry of Commerce and Industry) measures inflation through WPI.
- It does not show the cost of living adjustment (COLA).
(2) CPI (CONSUMER PRICE INDEX)-
- It measures the variation in the inflation rate in the retail market. CPI is the rate of inflation that affects all the individuals and the common man of India.
- It includes both gods and services.
- It shows the cost of living adjustment (COLA) because it measures prices at the retail level.
- CPI inflation is measured by the NSO ( National Statistical Organization).
(3) GDP DEFLATOR-
It is the ratio of nominal GDP to the real GDP in percentage. The quality-wise GDP deflator is the best measure of inflation.
Hopefully, you gained some extra info from this article on Meaning of Inflation, Types, and Measures…
Read more…
Unemployment- types and causes
Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology
Nice.
thankyou dear
Welcome..